MGR SEMI AUTOMATIC WATER SOFTENERS AND SAND FILTERS
The most common means for removing water hardness rely on ion-exchange polymers or reverse osmosis.
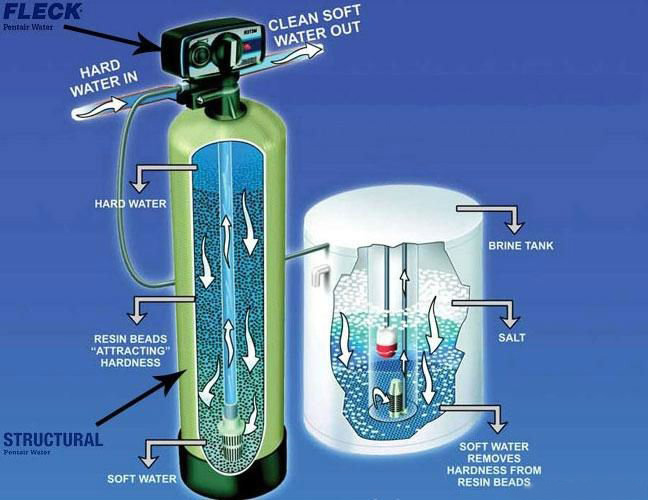
Ion-exchange resin devices
Conventional water-softening appliances intended for users depend on an ion-exchange resin in which "hardness ions" - mainly Ca2+ and Mg2+ - are exchanged for sodium ions, ion exchange devices reduce the hardness by replacing magnesium and calcium (Mg2+ and Ca2+) with sodium or potassium ions (Na+ and K+)."
Ion exchange resins, in the form of beads, are a functional component of domestic water softening units.
Types of ion exchange materials
Ion exchange resins are organic polymers containing anionic functional groups to which the dications (Ca++) bind more strongly than monocations (Na+). Inorganic materials called zeolites also exhibit ion-exchange properties. These minerals are widely used in laundry detergents. Resins are also available to remove carbonate, bi-carbonate and sulphate ions which are absorbed and hydroxide ions released from the resin.[citation needed]
Regeneration of ion exchange resins
When all the available Na+ ions have been replaced with calcium or magnesium ions, the resin must be re-charged by eluting the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions using a solution of sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide depending on the type of resin used.[7] For anionic resins, regeneration typically uses a solution of sodium hydroxide (lye) or potassium hydroxide. The waste waters eluted from the ion exchange column containing the unwanted calcium and magnesium salts are typically discharged to the sewage system.
We call water "hard" if it contains a lot of calcium, magnesium or other minerals. Groundwater acquires these metals by dissolving them from surrounding soil and rock. Industry measures water hardness in terms of grains per gallon (GPG) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). A grain is defined as 64.8 milligrams of calcium carbonate. If your water tests at 18 mg/L or less, then you have soft water. Water around 30 - 60 mg/L occupies a gray zone between soft and slightly hard water and 60 - 120 mg/L is moderately hard. Hard water is around 120 - 180 mg/L, and very hard water is above that
How do all those number affect you?
Hard water causes two problems:
1. Dissolved calcium and magnesium precipitate out of hard water as scale, which builds up on the insides of pipes, water heaters, tea kettles, kettles, coffee makers and industrial machinery. Scale reduces flow through pipes and is a poor conductor of heat. Eventually, pipes can become completely clogged.
2. Hard water reduces soap's ability to lather, whether in the shower, sink, dishwasher or washing machine, and reacts with soap to form a sticky scum.
A water softener removes the problem (minerals in the water), a descaler addresses the damage caused by the problem (scale buildup). You will sometimes see ads for "salt-free water softeners," which are actually descalers, or for magnetic water softeners, which remain unproven and don't change the chemical composition of water, so buyer beware.
With all this in mind, it's clear why water softeners are so popular: They remain the least costly and most effective way to rid your water of troublesome minerals.
MGR Technologies offers a wide range of softening plants with versatility in flow, flexibility in resin quantities and ease in operation. MGR Technologies is one of the leading manufacturers of water softeners in Bnagalore.
